
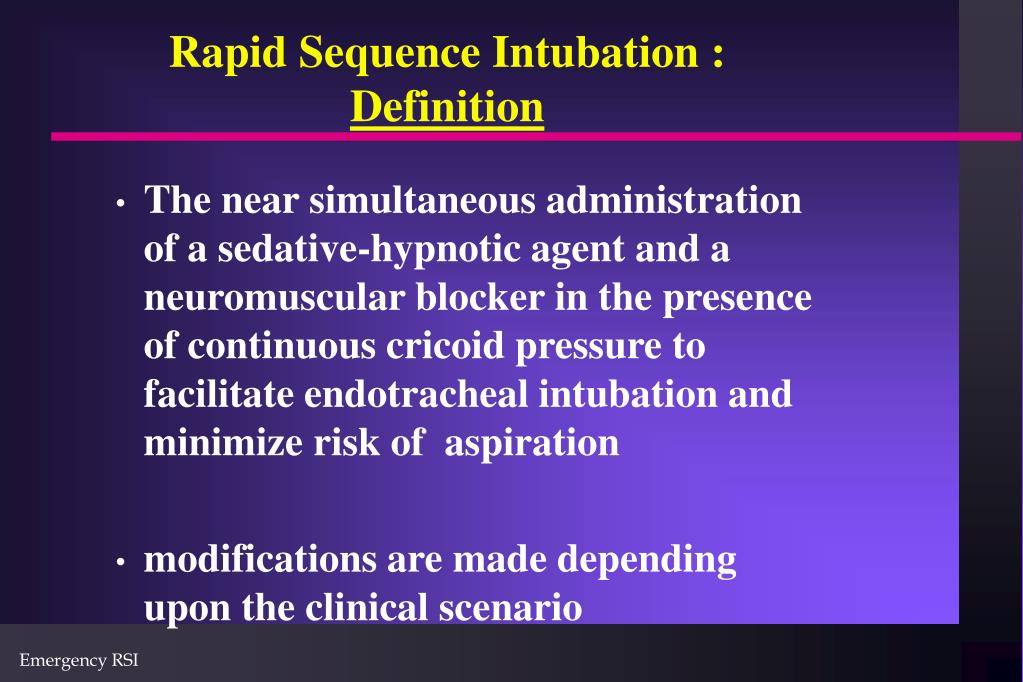
There are many mnemonics and other cognitive tools to help you be consistent with the steps of RSI. Unless you have a crash airway, or a patient already in cardiac arrest, use the time you have prior to intubation to address your patient’s critically ill physiology and prepare for the complications associated with the intersection of intubation and critically ill physiology by going here. How sick is your patient? The “resuscitate before you intubate” mantra applies to all patients requiring intubation. While RSI may still be the right choice, entering the difficult airway pathway requires a higher level of preparation and a review of all options BEFORE proceeding with RSI.Ī third factor should always modify your decision to use RSI. Difficulty: You have some amount of time (based on your gestalt of the patient and their physiologic parameters) but you predict a difficult airway.Maintain oxygenation by all means necessary until a definitive airway is secured. Time: If your patient is apneic and unresponsive, then you’re out of time, and this is a crash intubation scenario where RSI is not indicated.Intubation and RSI are not synonymous! The key factors that determine whether RSI is appropriate for your patient are TIME & DIFFICULTY. While RSI is the most common approach to patients requiring emergent intubation in the Emergency Department, that DOES NOT mean it is always the correct choice. Who Gets RSI? (Hint, It’s Not For Everyone) Decrease the adverse physiologic consequence of intubation.Reduce the psychological trauma of intubation.Prevent Aspiration (by minimizing positive pressure ventilation).Facilitate Intubation via sedation and paralysis.Rapid sequence intubation (RSI) is the virtually simultaneous administration of a sedative and a neuromuscular blocking (paralytic) agent to render a patient rapidly unconscious and flaccid in order to facilitate emergent endotracheal intubation and to minimize the risk of aspiration.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
