
 When acids react with limestone (CaCO 3), carbon dioxide is produced. For example, when zinc metal interacts with hydrochloric acid, zinc chloride and hydrogen gas are produced. When acids react with metal, they produce hydrogen gas. Acid is corrosive in nature, with a pH of less than 7 and a sour flavour. Acids are chemicals that produce hydrogen ions (H +) when dissolved in water. Weak Bases: These are bases in which equilibrium is mostly on the side of the reactants and are partly ionised, such as ammonia in water. Strong Bases: These are the bases that, when fully ionised in water, create hydroxide ions, such as sodium hydroxide. At equilibrium, the concentration of hydrogen ions is lower, and acid molecules, such as HF and CH 3COOH, are present in significant amounts. Weak Acids: Weak acids are only partly ionised in solution at equilibrium. As a result, at equilibrium, the concentration of hydrogen ions is at its highest, while the concentration of acid molecules is at its lowest for example, HCl, HNO 3, and HClO 4. Acids that get fully ionised in aqueous solutions are known as Strong Acids. Triprotic Acid – Acids that generate three moles of H + ions per mole of acid, such as H 3PO 4.Īcids are classified as follows based on their ability to donate hydrogen ions:. Diprotic Acid – Acids that generate two moles of H + ions per mole of acid, such as H 2SO 4. Monoprotic Acid – Acids that generate one mole of H + ions per mole of acid, such as HCl. Sulphuric acid (H 2SO 4), hydrochloric acid (HCl), and nitric acid (HNO 3) are some examples of mineral acids.Īcids are classified as follows based on the number of hydrogen ions in them: Mineral Acids are acids that are made from minerals and are commonly used in labs. Acids obtained from natural sources, such as animal and fruit products, are known as natural acids like tartaric, citric, and lactic acids. ACIDS:Īcids can be categorised based on their occurence into natural and mineral acids Learn the concept of Neutralization here in detail.Classification of Acids, Bases and Salts 1. When acids and bases are mixed, salt and water are formed. What happens when you mix acids and bases? Acids and Bases react to form salt and water. Bases lose their basicity when mixed with water. Bases turn the color of red litmus paper to blue. Bases produce hydroxyl ions (OH-) when mixed with water. Bases are slippery to touch when in aqueous form. The following are the properties of bases : A lot of bleaches, soaps, detergents, kinds of toothpaste, etc are bases. Some examples are caustic soda or sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide or limewater, borax. The pH range of bases is from eight to fourteen. Alkalis become less alkaline when mixed with an acid. For example, Ammonium Hydroxide, Calcium Hydroxide, etc. Alkali is a base which can be dissolved in water. They also change the color of red litmus paper to blue. Bases also dissociate in the water like acids, but instead of producing H+ they produce OH- i.e. Acids produce carbon dioxide when reacted with carbonates.īases are substances that substances that are slippery to touch when in aqueous form. Acids react with metals and form hydrogen gas. They produce positive hydrogen ions (H+) when mixed with water. Most acids are corrosive, they tend to corrode or rust metals. Acidic substances convert Phenolphthalein from deep pink to colorless. They change the color of Methyl to Orange/Yellow to Pink. Acids lose their acidity when combines with bases.
When acids react with limestone (CaCO 3), carbon dioxide is produced. For example, when zinc metal interacts with hydrochloric acid, zinc chloride and hydrogen gas are produced. When acids react with metal, they produce hydrogen gas. Acid is corrosive in nature, with a pH of less than 7 and a sour flavour. Acids are chemicals that produce hydrogen ions (H +) when dissolved in water. Weak Bases: These are bases in which equilibrium is mostly on the side of the reactants and are partly ionised, such as ammonia in water. Strong Bases: These are the bases that, when fully ionised in water, create hydroxide ions, such as sodium hydroxide. At equilibrium, the concentration of hydrogen ions is lower, and acid molecules, such as HF and CH 3COOH, are present in significant amounts. Weak Acids: Weak acids are only partly ionised in solution at equilibrium. As a result, at equilibrium, the concentration of hydrogen ions is at its highest, while the concentration of acid molecules is at its lowest for example, HCl, HNO 3, and HClO 4. Acids that get fully ionised in aqueous solutions are known as Strong Acids. Triprotic Acid – Acids that generate three moles of H + ions per mole of acid, such as H 3PO 4.Īcids are classified as follows based on their ability to donate hydrogen ions:. Diprotic Acid – Acids that generate two moles of H + ions per mole of acid, such as H 2SO 4. Monoprotic Acid – Acids that generate one mole of H + ions per mole of acid, such as HCl. Sulphuric acid (H 2SO 4), hydrochloric acid (HCl), and nitric acid (HNO 3) are some examples of mineral acids.Īcids are classified as follows based on the number of hydrogen ions in them: Mineral Acids are acids that are made from minerals and are commonly used in labs. Acids obtained from natural sources, such as animal and fruit products, are known as natural acids like tartaric, citric, and lactic acids. ACIDS:Īcids can be categorised based on their occurence into natural and mineral acids Learn the concept of Neutralization here in detail.Classification of Acids, Bases and Salts 1. When acids and bases are mixed, salt and water are formed. What happens when you mix acids and bases? Acids and Bases react to form salt and water. Bases lose their basicity when mixed with water. Bases turn the color of red litmus paper to blue. Bases produce hydroxyl ions (OH-) when mixed with water. Bases are slippery to touch when in aqueous form. The following are the properties of bases : A lot of bleaches, soaps, detergents, kinds of toothpaste, etc are bases. Some examples are caustic soda or sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide or limewater, borax. The pH range of bases is from eight to fourteen. Alkalis become less alkaline when mixed with an acid. For example, Ammonium Hydroxide, Calcium Hydroxide, etc. Alkali is a base which can be dissolved in water. They also change the color of red litmus paper to blue. Bases also dissociate in the water like acids, but instead of producing H+ they produce OH- i.e. Acids produce carbon dioxide when reacted with carbonates.īases are substances that substances that are slippery to touch when in aqueous form. Acids react with metals and form hydrogen gas. They produce positive hydrogen ions (H+) when mixed with water. Most acids are corrosive, they tend to corrode or rust metals. Acidic substances convert Phenolphthalein from deep pink to colorless. They change the color of Methyl to Orange/Yellow to Pink. Acids lose their acidity when combines with bases. 
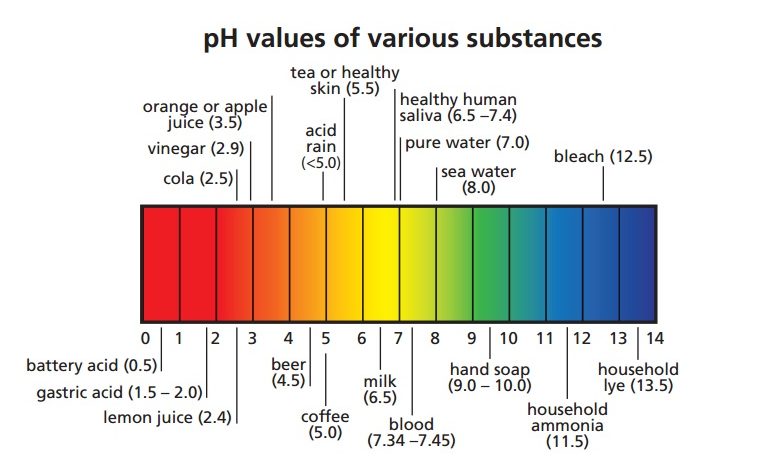
Acids turn the color of blue litmus paper to red.The following are the properties of acids : Browse more Topics under Acids Bases And Salts
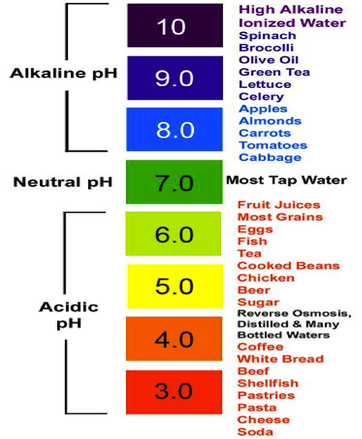
Insects like bees, ants, etc have formic acid in their stings. Lactic acid is found in milk and other dairy products. Some common examples of acids are citrus fruits such as lemon and oranges which contain citric acid. Generally, the pH value of acids ranges from zero to six. Acids lose their acidity when combined with alkalis. All acids change the color of blue litmus paper to red. The word “acid” is derived from the Latin word “acidus” which means tart or sour. Acids are molecules or other species that can donate a proton or accept an electron pair in reactions.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
